(Visited 3.407 times, 1 visits today)
Males are black with white cheek whiskers that have a more woolly appearance than the Southern White-Cheeked Gibbon. Females are yellowish-brown and the crown color ranges from dark brown to black, they are very similar in appearance to the Northern White-Cheeked Gibbon with no known consistent color variations between the species.
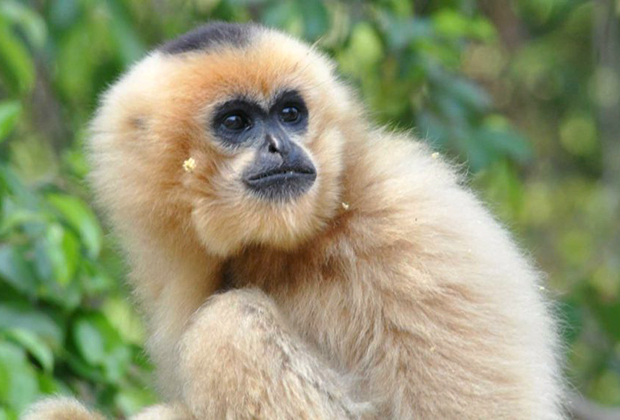
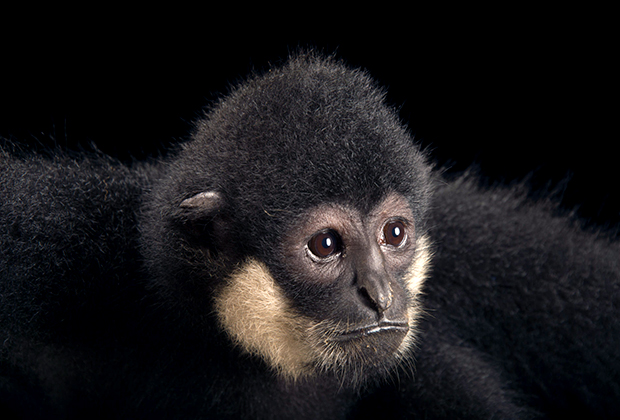
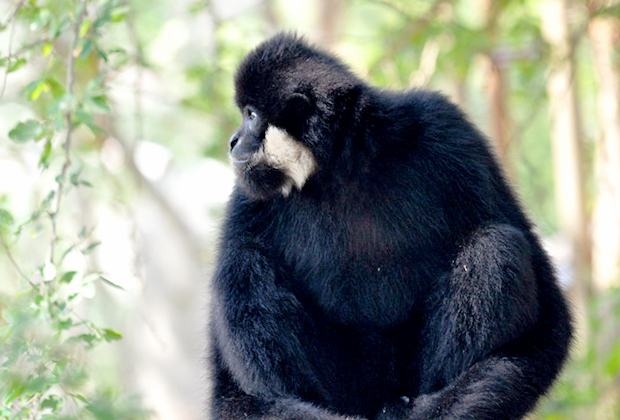



Found in Central Laos and Central Vietnam.
The Southern White-Cheeked Gibbon prefers primary lowland forest, tall primary tropical broadleaf and karst forest. There has been little research done on this species, but diets and social organization are likely similar to the other crested gibbons.
The main threat to this species is hunting, predominantly for the pet trade, and to a lesser extent for traditional medicine and local consumption. Additionally they are threatened by habitat fragmentation, especially in Vietnam.
The species is listed in the 2007 Vietnam Red Data Book as ‘Endangered’ and is protected by law under Decree 32/2001 ND-CP: 1B.
This species is threatened with extinction and international trade is permitted only in exceptional circumstances.
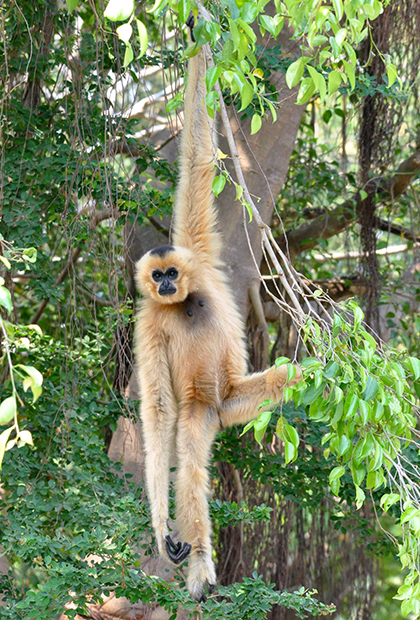


Established in 1993, EPRC is a not for profit project dedicated to the rescue, rehabilitation, breeding, research and conservation of Vietnam’s endangered and critically endangered primate species.
© Endangered Primate Rescue Center 2020
Website by MINIMUMMEANS